- What is conformity assessment? When is it required?
- What conformity assessment procedures are available at IEC?
- First-, second-, or third-party conformity assessment: a matter of trust.
- Declaration of conformity: compliance with specified requirements.

Conformity Assessment – the Free Flow of Goods Worldwide
What is conformity assessment?
When it comes to the assessment procedure, the economic operator (for example, the manufacturer) examines whether the requirements described in legislation, technical norms, and standards have been satisfied either in part or as a whole by the products and/or processes to be assessed.
In order to determine the applicable requirement, it is necessary to define the starting point for the conformity assessment in question:
- statutory (European perspective)
- or normative (international perspective)
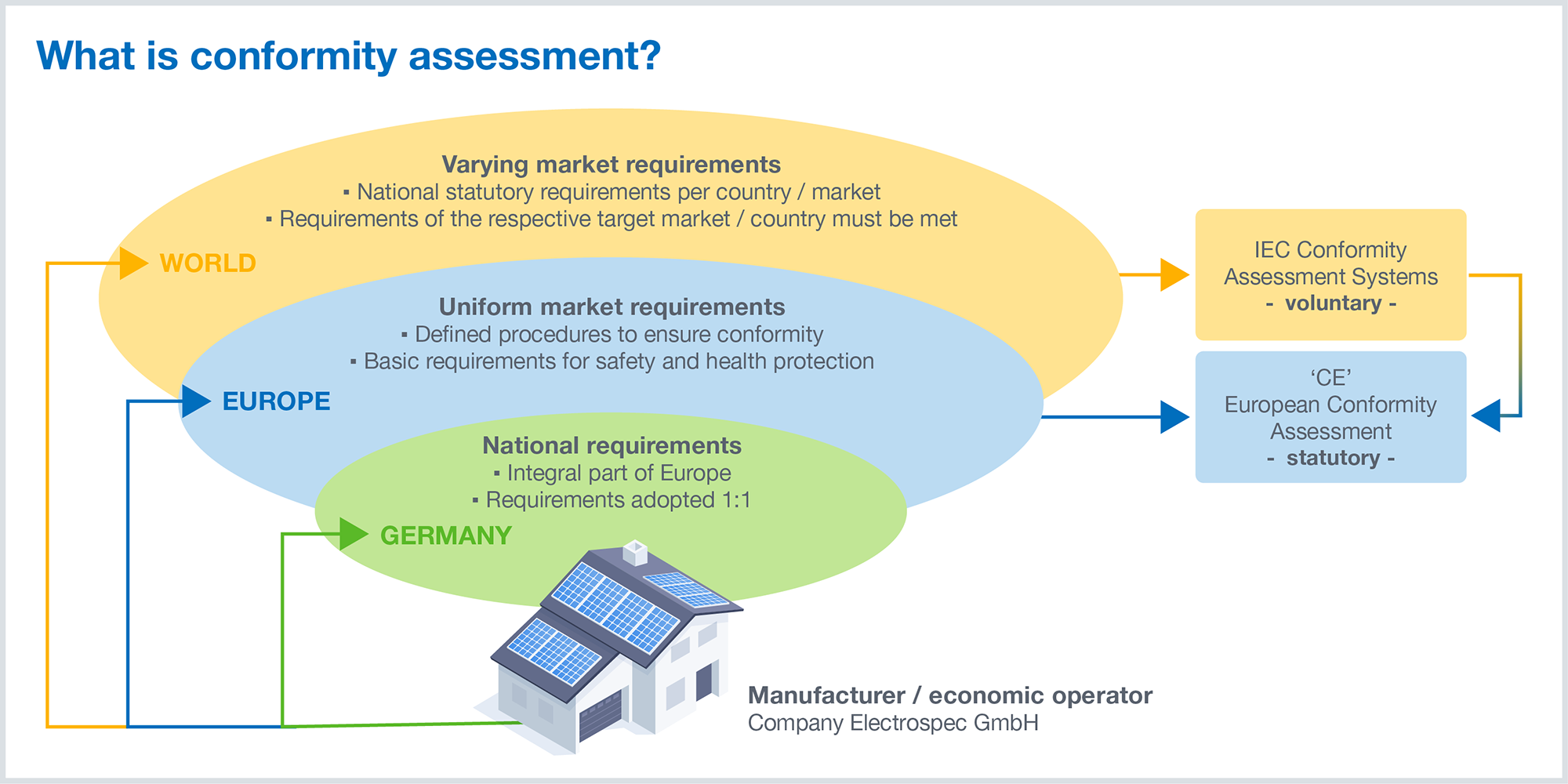
Within the legal framework of the EU, conformity assessment is defined as: “the process demonstrating whether specified requirements relating to a product, process, service, system, person or body have been fulfilled” (European Decision 768/2008). The requirements are thus prescribed by the legal framework of the target market.
Manufacturers are able to find the applicable requirements for the European target market for each product group on the EU website.
In terms of international norms, conformity assessment is defined as a “demonstration that specified requirements [...] relating to a product [...], process, system, person or body are fulfilled” (DIN EN ISO/IEC 17000 Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles). Norms and standards regulate these requirements with regard to the safety and performance of, for example, products or processes.
Conformity in technology and electrical engineering therefore means that a product or machine shall comply with the statutory requirements set out, for example, in the Machinery Regulation (formerly Machinery Directive), the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC). Further legal requirements can be found, for example, in the ATEX Directive on potentially explosive atmospheres and in the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) regarding the safety of pressure equipment/assemblies.
What is conformity assessment?
Conformity assessment – simply and understandably explained in a nutshell. In other words, conformity means “compliance.” Compliance is assessed during conformity assessment with regard to requirements arising from legislation and the technical implementation of standards. Products and services are like a promise when it comes to their properties (e.g., quality, safety, compatibility, interoperability, etc.). This makes it all the more important that this promise is kept. Conformity assessment delivers precisely that!
When is a conformity assessment required?
A conformity assessment is required if requested by the one or other party; for example, by the contracting party to an agreement in a B2B transaction, or by law.
Conformity assessment procedures in B2B transactions
Two companies would like to come to an agreement for the delivery of a product. The manufacturer is based in Germany and the product is to be sold in the USA. As a rule, the statutory requirements of the target market (in this case the USA) always apply.
However, the purchasing company stipulates in the agreement that the product must undergo a conformity assessment before delivery to the USA. Due to the international nature of this cooperation, the customer also specifies that the product must be tested in accordance with the IECEE conformity assessment procedure. IECEE stands for “IEC System of Conformity Assessment Schemes for Electrotechnical Equipment and Components.”
The manufacturing company is responsible for initiating the conformity assessment procedure. At the end of this process a (conformity) certificate is then issued which confirms that the respective requirements have been met. By successfully completing the IECEE conformity assessment procedure, the manufacturer based in Germany establishes a basis of trust for the product – and thus for the manufacturer’s company as well. In this case, the customer in the U.S. can assume that the product meets the requirements of international norms and standards when it comes to both safety and performance.
Legal requirements for conformity assessment
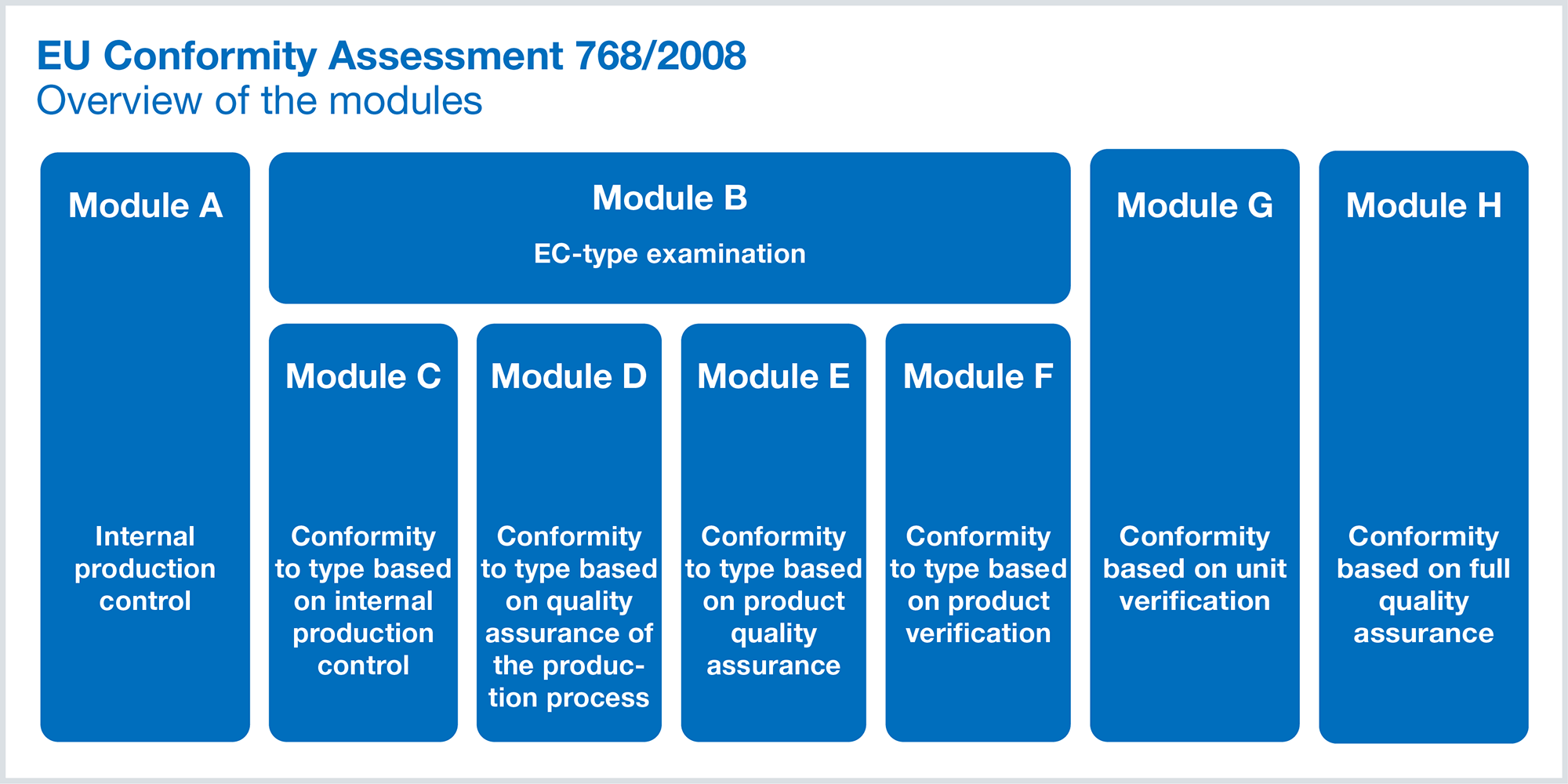
Conformity assessment requirements can be found in European directives and regulations, such as the Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU or the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 2014/30/EU. What both European directives have in common is that their requirements are based on a modular conformity assessment procedure in accordance with European Decision 768/2008.
Market players, such as manufacturers and distributors, are only required to satisfy the conformity assessment modules that apply to the products or supplier commodities to be tested. However, this requires that the structural elements of the modular conformity assessment procedure that apply to the respective products or supplier commodities are determined at the outset. These can be found in the respective EU directives and regulations on CE marking, tailored to the respective scope of application.
What is the relationship between conformity assessment, quality management, and quality assurance systems?
Quality management systems (QMS), quality assurance systems (QAS) and conformity assessments help to ensure that products not only meet the company’s internal quality requirements, but the respective external legal and regulatory requirements as well. A QAS is mandatory in the conformity assessment procedures for a number of products. A QMS is not explicitly required, but the conformity assessment procedure in fact benefits from an in-house QMS.
What is the difference between a quality assurance and a quality management system?
The QA system aims to monitor and ensure implementation (of product quality specifications, for example).
A QM system is fundamentally designed for prevention and process optimization.
Which conformity assessment modules require a quality assurance system?
Modules D, E and H of European Decision 768/2008 provide examples; each of which requires a quality assurance system (QA system) for production, products, or a comprehensive QA system in general.
The specified modules stipulate that the audit team involved shall have at least one member with both knowledge of and experience with QA systems. This implies that a QM system is advantageous when it comes to satisfying the module requirements – however, there is also no explicit obligation to have one. A quality assurance system, on the other hand, is indeed required for the specified modules.
Detailed descriptions can be found in European Decision 768/2008 in ANNEX II.
What conformity assessment procedures are there?
At the statutory level, the CE marking exists within the New Legislative Framework (NLF) in Europe, which indicates a successful conformity assessment procedure. The CE marking regulates various regulations and directives with regard to several different aspects, such as safety, performance, functional stability, etc., and requires a conformity assessment from the addressee in each case. The latter are usually referred to as economic operators (manufacturers, authorized representatives, importers, and distributors).
At the level of international standardization there are four IEC conformity assessment systems. These IEC conformity assessment systems are crucial for ensuring the global acceptance and market availability of products, while also guaranteeing compliance with international norms and standards.
Um den Warenfluss im EU-Binnenmarkt zu verbessern und die Bedingungen für das Inverkehrbringen einer breiten Palette von Produkten auf dem EU-Markt zu erleichtern, wurde 2008 der neue Rechtsrahmen verabschiedet. Es handelt sich um ein Maßnahmenpaket, das die Marktüberwachung verbessern und die Qualität der Konformitätsbewertungen steigern soll.
IECEE: Electrotechnical Equipment and accessories
IECEE (IEC System for Conformity Assessment Schemes for Electrotechnical Equipment and Components) is used to recognize test reports and certificates for electrical and electronic products. The aim is to facilitate international trade by reducing trade barriers and recognizing tests and certifications in different countries. IECEE covers a wide range of products, including household appliances, IT equipment, medical devices, and more.
IECEx: Equipment and services for potentially explosive atmospheres
IECEx (IEC System for Certification to Standards Relating to Equipment for Use in Explosive Atmospheres) is used to certify equipment, services, and personnel that are operated in potentially explosive atmospheres. It includes product certifications (IECEx Equipment Certification), certifications of services such as maintenance and repair (IECEx Service Facilities Certification) and the certification of personnel (IECEx Certification of Personnel Competence) and has been expanded to include hydrogen.
IECRE: Equipment used for renewable energies
IECRE (IEC System for Certification to Standards Relating to Equipment for Use in Renewable Energy Applications) is employed for the conformity assessment of equipment and systems in the field of renewable energies such as wind energy, solar energy, and marine energy. It ensures that equipment and systems comply with the relevant international standards and offer a high level of safety, reliability, and performance.
IECQ: Quality assessment of components and processes
IECQ (IEC Quality Assessment System) is a quality assessment system for electronic components and related materials and processes. The system primarily consists of three spheres of activity: Circular Economy Services, Supply Chain Services, and Component Product Services. It includes various programs such as IECQ HSPM (Hazardous Substance Process Management) for compliance with environmental regulations and IECQ ITL (Independent Testing Laboratory) for certifying independent testing laboratories, and will be used as a horizontal system far beyond the boundaries of electrical engineering.
Types of conformity assessment
Conformity assessment is often equated with the certification process itself – but this is only true in part. When it comes to conformity assessment requirements, there are different types that relate to the entity being assessed and which define different criteria with regard to product safety.
First party assessment by manufacturing and placing companies
The initial assessment is aimed at manufacturers or economic operators responsible for placing a new product on the market. With a declaration of conformity, they confirm that the product in question complies with the respectively applicable requirements. The level of safety is lower than in the case of second- and third-party assessments, as customers and consumers only have to rely on the information provided by the manufacturer.
The advantage lies in rapid market access and the avoidance of technical barriers to trade wherever possible. This process requires a certain amount of trust on the part of the manufacturing companies.
A second party assessment is independent of the manufacturing company
The second-party assessment body involves the respective customer or operator in the B2B arrangement. The conformity assessment may, for example, be divided between the customer or operator and the economic operator who places the respective product on the market. Alternatively, the conformity assessment may also be carried out entirely by the second-party assessment body. As a rule, the second-party assessment body checks for conformity as such on the basis of the declaration of conformity or the manufacturer’s declaration as well as the results of the processes and documentation – provided that such exchange has been contractually agreed in advance. The level of safety is higher than in the case of the first party, as the conformity assessment is, for example, not carried out exclusively by the manufacturer.
Certification by a third-party assessment body
The third-party assessment body is a certification body that operates independently and conducts objective assessment.
The level of safety in this case is therefore the highest compared to the first and second-party assessments. This means that certification is also very important for customers and consumers. And, once again, this highlights the global significance of certifications based on the four international conformity assessment systems of the IEC.
Specially regulated conformity procedures within the EU
In Europe, the legally regulated area applies to products in particular. In such cases the scope of application as well as applicable EU directives/regulations for CE marking must be determined and implemented. The same applies to the relevant norms and standards.
In many cases this involves a first-party conformity assessment. A third-party conformity assessment is carried out if specified in the relevant statutory requirement. Voluntary support from a notified body may be requested even in the case of a legally required first-party conformity assessment; however, the same applies to a second-party conformity assessment as well. This form is normally used when manufacturers from smaller companies are unable to meet the requirements on their own due to a lack of expertise or resources.
In addition to the area that is conclusively regulated by legislation, there is also an area that is not conclusively regulated by law. The German Product Safety Act – which is currently undergoing revision – is important in this regard. This revision is accompanied by the new General Product Safety Regulation [GPSR] at EU level, which takes effect on December 14, 2024.
Conformity assessment vs. declaration of conformity: What is the difference?
Unlike conformity assessment, a declaration of conformity is a document that states that a product, for example, complies with the specified requirements.
Conformity assessment procedures, which include development, design, risk analysis and assessment, documentation, testing, test processes, and audits, enable manufacturers to issue a declaration of conformity for their products, processes, or services.
This is an official document that confirms that a product complies with the relevant statutory and, where applicable, normative requirements based on norms and standards. The declaration of conformity is thus often a necessary part of the market access process for many products, especially in regulated sectors such as electrical engineering, medical devices, mechanical engineering, and toys.
Examples of declarations of conformity include
- CE marking (European Union)
- FCC Declaration of Conformity (USA) and
- Declarations for products that fall under the RoHS Directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances).
The declaration of conformity thus represents a central element of product safety and quality assurance systems worldwide.
Conclusion: Conformity for safety and quality
Conformity assessment is a key process that ensures that products, processes, or services meet the specified statutory and normative requirements. Different economic areas (EU, USA, China, etc.) may have different statutory requirements for the provision of products.
The conformity assessment procedure comprises a wide range of activities that accompany development, in parallel with testing and documentation processes. In addition to statutory requirements, the assessment procedures in electrical engineering also take standards prepared by experts in the DKE standardization committees into consideration.
These conformity assessment procedures ensure the safety and reliability of electrical equipment, electrical components, systems and products. The declaration of conformity, which is the result of the conformity assessment, officially confirms that the necessary requirements have been met and thus provides for market approval, in particular within the EU through CE marking.